SINUS LIFT
A sinus lift (a sinus augmentation) is surgery that adds bone to your upper jaw in the area of your molars and premolars to make it taller. The bone is added between your jaw and the maxillary sinuses, which are on either side of your nose. To make room for the bone, the sinus membrane has to be moved upward, or "lifted." A sinus lift usually is done by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon or a periodontist.


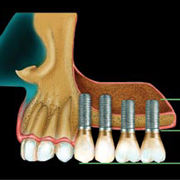

It can happen that there is no longer enough bone in the molar area of the maxilla in the direction of the floor of the sinus because of the bone atrophy after tooth loss. As bone augmentation in this region is possible only with difficulty, a method was developed in which the floor of the sinus is raised and bone is inserted into the cavity produced, without injuring the mucosa of the sinus, which leads to an effective increase in the bone in the molar maxillary region. This operation is called a sinus lift. This operation can be carried out under local anaesthesia and is done through the mouth so that there are no scars on the face. The sinus lift operation can often be done at the same time as the insertion of dental implants. The bone material which is inserted corresponds to that described already for bone augmentation.
Procedure
The oral surgeon will cut the gum tissue near your premolars and molars. The tissue is raised, exposing the bone. A small, oval window is opened in the bone. The membrane lining the sinus on the other side of the window separates your sinus from your jaw. This membrane is gently pushed up and away from your jaw. Granules of bone-graft material are then packed into the space where the sinus was. The amount of bone used will vary, but usually several millimeters of bone is added above the jaw.
Once the bone is in place, the tissue is stitched closed. Your implants will be placed four to nine months later, depending on the graft material that was used. This allows time for the grafted material to mesh with your bone.




